摘要
\(R\) :相关系数(correlation coefficient),即皮尔森相关系数,值位于 -1 到 1 之间,即负相关和正相关,绝对值越大表明相关性越强,P值越小越相关。
\(R^2\) :决定系数(coefficient of determination),\(R^2\) 值越接近 1,吻合程度越高,越接近 0,则吻合程度越低。
决定系数 = 相关系数平方
皮尔森相关系数
皮尔森相关系数也称皮尔森积矩相关系数(Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient) ,是一种线性相关系数,是最常用的一种相关系数。记为 R,用来反映变量X和变量Y的线性相关程度,R 值介于-1到1之间,绝对值越大表明相关性越强。[1]
适用连续变量。
相关系数 与相关程度一般划分为
0.8 - 1.0 极强相关
0.6 - 0.8 强相关
0.4 - 0.6 中等程度相关
0.2 - 0.4 弱相关
0.0 - 0.2 极弱相关或无相关
原假设:两者不存在相关性 P值小,即我们观察的样本(不存在相关性)发生的概率小,存在相关性的概率大,如果原假设成立即不存在相关性,那么我们这个样本就很极端很显著。
相关系数绝对值越大,越相关,P值越小越相关。
scipy.stats.pearsonr(x, y, *, alternative='two-sided')
:[2]
1 | # Python实现 |
numpy.corrcoef(x, y=None, rowvar=True, bias=<no value>, ddof=<no value>, *, dtype=None)
Return Pearson product-moment correlation coefficients.[5]
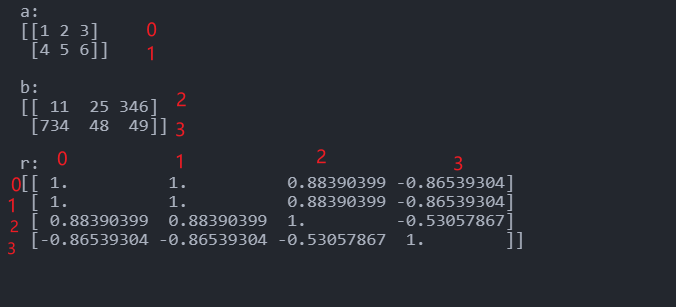
这里计算的是特征与特征(行与行/列与列)的相关系数。
1 | import numpy as np |
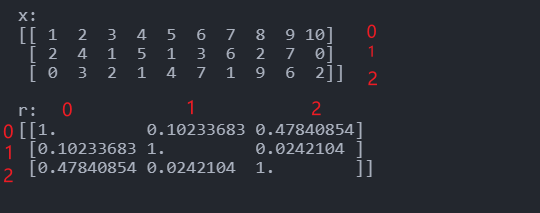
1 | a = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]) |
线性回归的R平方
线性回归后得到的 R 平方和使用皮尔森相关求得的 R 再平方数值上面是一样的。[3]
R平方:决定系数,反应因变量的全部变异能通过回归关系被自变量解释的比例。\(R^2\) 值越接近1,吻合程度越高,越接近0,则吻合程度越低。\(R^2\) 作为相关系数,一般机器默认的是\(R^2\) >0.99,这样才具有可行度和线性关系。[4]